|
telescopeѲptics.net
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪▪▪▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪ CONTENTS
◄
4.8.1. Testing optical
quality
▐
4.8.3. Ronchi test
► 4.8.2. Foucault test
PAGE HIGHLIGHTS Invented by the French scientist Leon Foucault in 1858, this ingenious test uses point source of light placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror (in practice, slightly to the side, so that the mirror focus is separated from the source, and focusing light can be intercepted without cutting off source of illumination), as illustrated on FIG. 52. The combination of simplicity and accuracy has made it the single most used test in the amateur telescope makers' circles.
If it is a sphere, a straight-edge shadow moves over the surface as the
KE cuts through the light converging to or diverging from the focus (A'); or the uniform, light-grayish
shadow spreads over the entire surface when the KE intercepts
converging cone at the focus,
producing
so called null (A).
This makes the test particularly well suited for quick and reliable
tests of spherical reflecting surfaces. Non-spherical surfaces produce
defocused, commensurate to their
conic, creating various shadow forms as the
KE moves
through the converging light near aberrated focus (B), with only
a single zone nulled, and the rest
of surface area split between darker and brighter areas (B', edge
zone nulled, patterns
generated by Mike Lindner's Foucault Simulator).
While long ago replaced with newer testing technologies in the
professional circles, Foucault test is still widely used by the amateurs.
The standard reference is How to make a telescope by Texereau;
more recent, A manual for amateur telescope makers, Leclaire.
Online, David Harbour's description is among the most detailed of the
Foucault test.
Programs for analyzing Foucault test data, such
as
SIXTEST
by Jim Burrows, are computer-era enhancement to the test's proven
value. More recent variants of the test include replacing KE with
a wire (wire test), the Foucault zonal mask by (Everest) pin-stick, or the
eye by a camera, taking shots of the entire mirror surface for
selected blade locations, which then can be analyzed with computer
software (automated, or Robo-Foucault, such as the
"semi-automated" version detailed by Mike Peck).
Foucault shadows do not offer an intuitive grasp; they are the consequence of the
knife edge cutting into the beam of reflected light being positioned differently
with respect to the zonal foci, which determines what part of the mirror will appear
illuminated, and how much. Geometry of rays below shows overcorrection, generated
by near-paraboloidal mirror with light source at the radius of curvature.
Looking, for example, at the best focus location, midway between the paraxial and marginal ray focus,
knife edge cutting into the beam of light up to the axis is positioned ahead of the marginal ray focus
(blue rays), but behind the paraxial ray focus (red). As a result, it is completely blocking light
from mirror top, and leaving mirror bottom open (since ray aberration geometry increases exponentially toward edge,
large separation of marginal vs. mid-zone rays corresponds to a relatively small outer zone,
which shows brightly illuminated). At the same time, it is blocking light from the bottom mid-zones,
while leaving top mid-zones open. This inevitable difference in the knife location vs. different zonal
foci produces pattern of subsequent dark, semi-dark and bright zones on the mirror. They are accompanied
with diffraction effects, generally small in comparison.
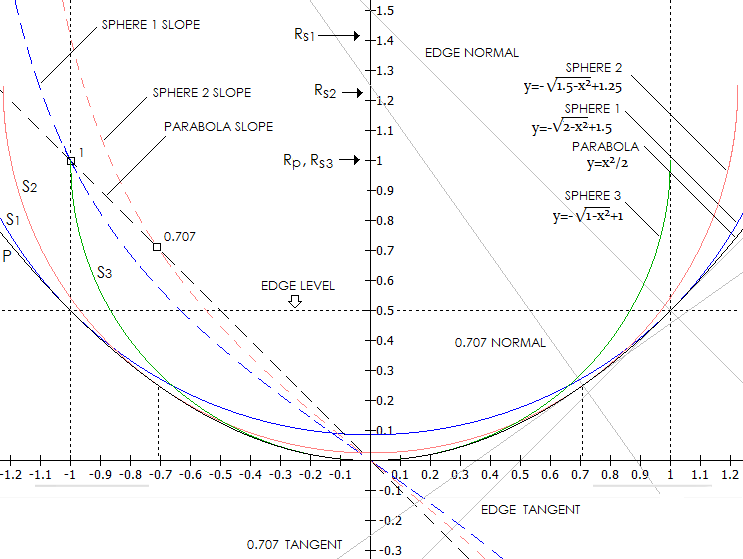
Due to inherent aberrations of the spherical mirror surface in imaging distant objects, paraboloid is preferred surface for telescope mirrors. Consequently, Foucault test is most often used in making paraboloidal mirrors. Ideally, paraboloid should be tested with collimated beam (i.e. for object at infinity), which is a null test for this conic. However, due to practical difficulty of producing collimated beam, it is usually tested with light source at the center of curvature (vertex radius). Since for non-spherical surface in such setup every zone has somewhat different focus location, the test consist in extracting the degree of deviation of the actual measured zonal foci from those corresponding to a perfect paraboloid. Longitudinal aberration for object (source) at the center of curvature (fixed source, moving knife edge) is given by:
LA = KDρ2/8F
= -K(ρd)2/R,
where K is the conic, D mirror diameter, ρ the
zonal (radius) height normalized to 1 for D/2=d, and F the mirror
focal ratio f/D (not to confuse with the actual test focal ratio, which
is 2F), f being the focal length,
half the vertex radius of curvature R (note that this applies
only for paraboloid, i.e. K=-1; f<R/2 for K>-1 and f>R/2 for K<-1). It
is measured with respect to paraxial focus, with the minus sign for K<0 indicating
that outer zones focus farther away than the central zone.
For source moving with the knife edge the LA is half as large as for
fixed source, i.e.
LA = KDρ2/16F = -K(ρd)2/2R These expressions are valid for most amateur mirrors. For very fast mirrors, inclusion of correction terms may be needed to maintain test accuracy.
Specific manner in which the data obtained by measuring deviations from
perfect zonal foci is used varies somewhat from one source to another. More complex method goes through
calculating residuals and using data reduction, while the simpler method works with direct
measurements of zonal deviations. The purpose of deriving residuals is to filter out the error in placing the reference point for the measurements vs. actual mirror center of curvature, which is hard to pinpoint. The next step is so called reduction, which is deducting residual of a selected zone from the rest of residual values. Its purpose is to reduce the value of residuals to an actual longitudinal differential between the measurements. Selection of the zonal value to be deducted is arbitrary; it is usually either the inner zone, the ~70% (ρ~0.7) or the outer zone. Obviously, the reduced LA value for selected zone is zero, which means that it is assumed to be a part of the perfect reference surface. If the actual measurements are identical to those for the perfect paraboloid, except for the reference point differential, the residuals for all zones would equal the reference point differential, and the reduced LA value would be zero for all. The reduced value LR are used to obtain relative transverse aberration, from RTA=-ρLR/2F. It is termed relative because it is based on longitudinal aberration relative to a chosen zonal focus. It is usually measured against, or expressed in units of the Airy disc diameter. The minus sign determines RTA value as positive for the longitudinal aberration LR relative to the reference focus extending away from the mirror, and vice versa. RTA is not to be confused with the transverse spherical aberration, because the two are generally different, i.e. relative transverse aberration in Airy disc diameters is generally smaller, possibly significantly, than the transverse spherical aberration for given value of conic deviation.
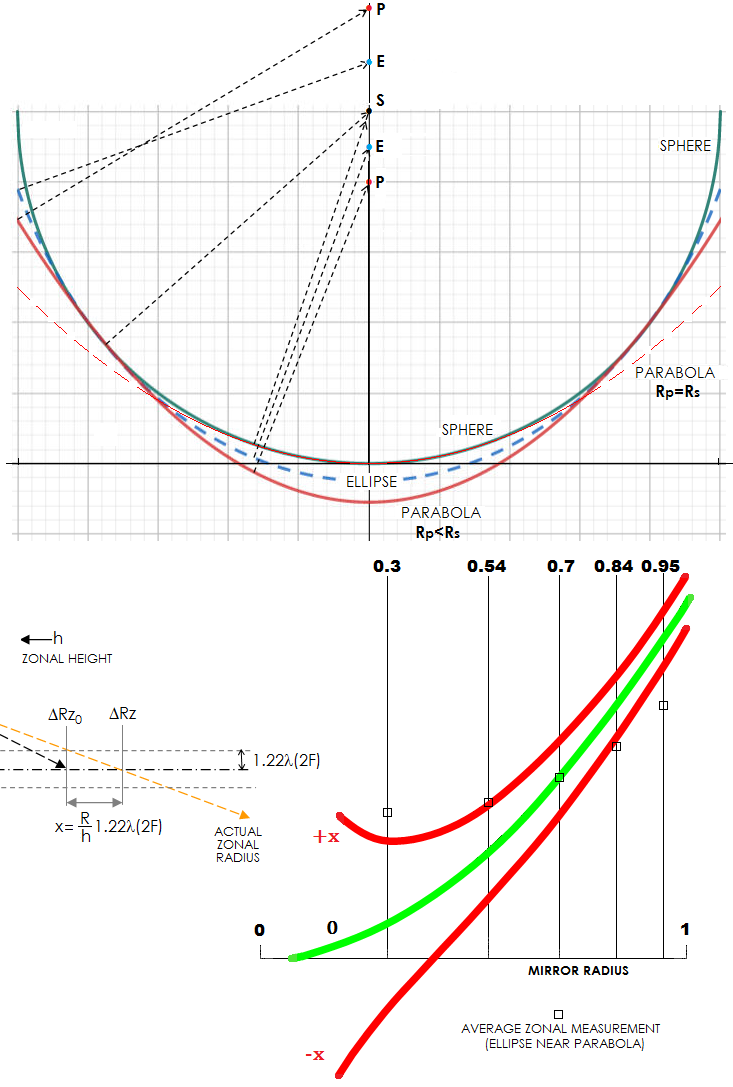
Choosing the inner zone for the reduction gives the respective reduced values 2.7mm, 1.5mm, 0.54mm and zero. They give the respective RTA as -0.243mm, -0.105mm, -0.045mm and zero. In units of the Airy disc diameter (2.44λF, or 0.0134mm for 550nm wavelength and the effective F=10), it is 18.1, 10, 3.6 and zero, in the same order. For comparison, full longitudinal spherical aberration for this mirror (for infinity focus) is -3.75mm, and its paraxial blur diameter is 0.375mm, or 27.9 Airy disc diameters. If the 70% zone is chosen for reduction, the relative longitudinal aberration values are 1.2mm, zero, -0.95mm and -1.5mm, and RTA is 0.108mm, zero, 0.048mm and 0.045mm (8, zero, 3.5, and 3.4 in Airy disc diameters), respectively. Nominally much better, despite being for the same surface. Obviously, the choice of reduction zone significantly influences nominal indicators of surface quality with the Foucault test, and the two test results are comparable only if using identical reduction zone. Choice of a different reduction zone will also give a different indication of which portion of mirror surface needs to be addressed. Choosing central zone indicates that all (other) zones focus short of the reference paraboloid, the higher zone the more so, hence that the surface needs to be corrected by polishing off nearly the entire surface, increasing toward the outer area. On the other hand, with reduction relative to the 70% zone, relative longitudinal aberration indicates the outer zone focusing shorter, and the two inner zones focusing longer. That indicates that the outer and inner zones need to be worked on, leaving 70% zone area out. With the outer zone being chosen for reduction, the indication would be that surface deviation increases toward mirror center. Since RTA can be used to construct the wavefront profile in zonal segments, with the wavefront zonal angular deviation from the reference wavefront's slope closely approximated by β=RTA/2R, R being the mirror radius of curvature, and the corresponding linear deviation of the aberrated wavefront Zβ, Z being the zonal width, the choice of reduction zone will also determine the resulting wavefront profile. Consequently, the best fit parabola for the outer, 70% and inner zone, will be one centered at the marginal focus (approximately), best focus and paraxial focus (approximately). The following is a graphic example of the main Foucault test parameters and relationships, illustrated with the actual surface being a sphere. If the sphere is, for instance, 150mm f/8 mirror, thus with radius of curvature R=2400mm, its longitudinal aberration at infinity focus is D/32F=0.586mm. With the object at the center of curvature, the wavefront incident on mirror surface coincides with it, and it is reflected straight back to the center of curvature. Thus, the longitudinal aberration is zero. However, if paraboloidal surface is desired, then the reference is a paraboloid of identical vertex radius, which would produce longitudinal aberration four times greater than that of the sphere at infinity focus, or 2.34mm. It varies with the square of zonal height, so taking for simplicity three off-center zones, 30-50, 50-65 and 65-75, hence of the respective zonal widths z1=20mm, z2=15mm and z3=10mm, with median heights (h) of 40, 57.5 and 70mm, their longitudinal aberrations (LA) are 0.67, 1.38 and 2.04mm, respectively.
Since the measured zonal sections of the sphere are perpendicular to the mid-zone radius, and all the radii project into the center of curvature, the shape of reconstructed wavefront approximates mirror surface. However, if the actual surface is desired paraboloid, projected zonal segments are perpendicular to the mean zonal radius (i.e. local radius of curvature of the paraboloid) do not converge to a single point (with moving source, Foucault test directly measures foci locations of these local, i.e. mean zonal radii, which in turn determine averaged zonal slope at the surface). As a result, sections of wavefront from any single point do not reflect off simultaneously. Since paraboloid's surface spreads out toward the edge, the incident wavefront originating, for instance, at the center of curvature, reaches outer zones latter, and those sections lag behind the inner wavefront portion. In effect, the wavefront reflected off the paraboloid flattens out relative to paraboloid's surface, and the differential between it and the wavefront produced by a sphere is double their zonal sagitta differential. There is a direct relationship between the degree of deviation of these two wavefronts (the actual one, and that of a perfect reference surface) and measured zonal deviations. From TA=(h/R)LA, the corresponding transverse aberrations for the three zonal LA readings with the above sphere, in the same order, are 0.011, 0.033 and 0.0595mm, and their zonal slope deviations, σ=(TA/R)z, are 0.0000917, 0.000206 and 0.00025mm. In units of λ=0.00055mm wavelengths, it is 0.17, 0.037 and 0.45λ. The total deviation is a simple sum of the three, or 0.99λ. This is nearly double the maximum surface differential between this sphere and its reference parabola of 0.52 wave (the figure is generally somewhat lower, due to the outer zone being averaged out). Assuming null at the zone 1, the corresponding relative transverse aberration is greatest at the zone 3, as RTA3=(TA3-TA1)/2.44λF (for the doubled Airy disc with object at the center of curvature, with F being the infinity focal ratio) - a disastrous 4.5 Airy disc radii. But this mirror is, in fact, near diffraction-limited. Taking mid-zone for the null nearly reduces the RTA in half, as does nulling at the outer zone. The 0.99λ wavefront error at the wavefront constructed from the measurements is not the actual error. In this case - and nearly any other - there is a parabola of slightly different radius, whose wavefront deviates less - often significantly so - from the constructed wavefront. It is called "best fit parabola". In this case, best fit paraboloid has slightly stronger curvature than one with vertex radius equal to that of the actual surface. It has identical sagitta to that of the sphere, touching the latter at the vertex and at the edge. The error vs. this parabola is reduced by a factor of 0.25, from 0.99λ down to 0.25λ. This is the final test result.
The only difference between sphere and a conic closer to a paraboloid is
that the latter does not have zonal foci coinciding at the center of
curvature. These foci are separated as for paraboloid, either in
somewhat smaller (prolate ellipsoid) or greater degree (hyperboloid with
conic less than -1.2), thus with smaller longitudinal aberration at each
zone.
As the schematic implies, limit to the zonal focus deviation is set by transverse aberration equaling Airy disc radius.
That allows for larger deviations for the lower vs. higher zones, in inverse proportion to the zonal height, which
is opposite to the value of longitudinal aberration, exponentially larger for higher vs. lower zones (dashed gray
lines show the focus differential limit proportional to the longitudinal aberration for given zonal height).
This, in effect,
allows for larger conic deviation from the paraboloid for the lower zones, but since the sagitta differential
is about as much smaller for the lower zones for any given conic, the surface deviation is approximately constant.
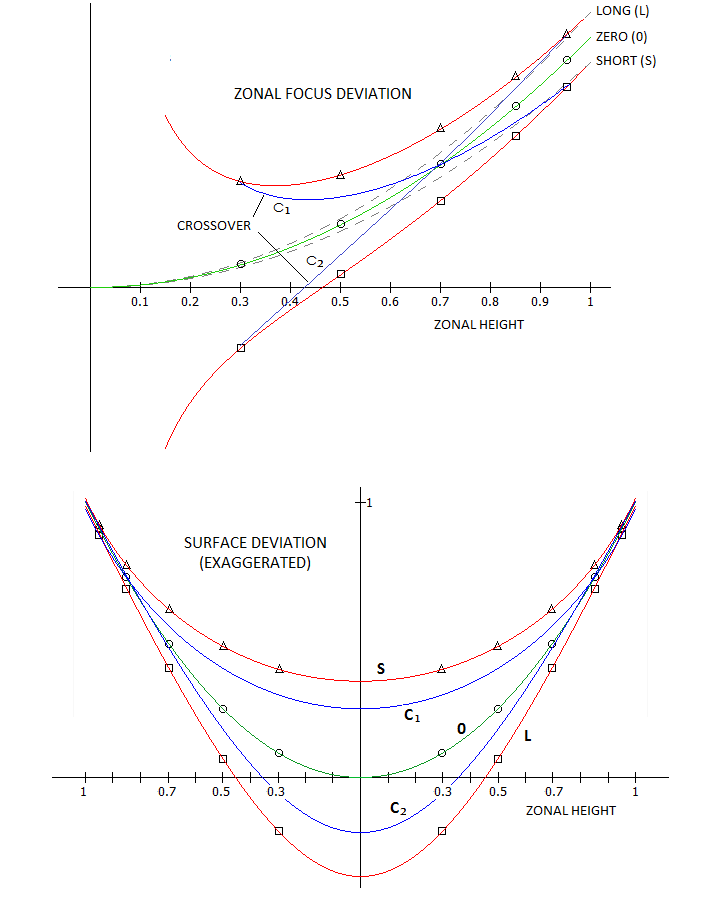
Graphs below illustrate form of surface deviation for the L-M graph with measured values coinciding with the positive
limit (H), with the negative limit (L) and a crossover line (C1/2). Deviations are greatly exaggerated
for clarity.
Measurements at the positive limit indicate generally weaker curvature, toward the prolate ellipse form, i.e.
undercorrection at infinity focus, while those at the negative limit indicate stronger overall curvature,
toward hyperboloid, i.e. overcorrection at infinity focus. The two crossover measurements, as the shape of the lines
connecting them implies, are similar to their limit-line counterparts, only somewhat shifted. As the
previous illustration shows,
their surface shape is either a near-paraboloid prolate ellipse, or hyperboloid, while the first two are what can
be called conicoids.
The zonal focus differential can be tied to the conic, since the relative deviation from the paraboloid's
longitudinal aberration for given zonal height are proportional to the conic value deviation from -1 (e.g.
10% longer LA implies that surface slope coincides with that of as much stronger conic, i.e. -1.1). The problem
is that any "zonal conic" represents only a small portion of the actual surface profile, unrelated to the values
for the other zones. Also, it is valid only under assumption that the vertex radius of curvature is constant,
and known. However, using technique described in "A Manual for Amateur Telescope Makers" by
Karine and Jean-Marc Lecleire, the zonal wavefront slopes indicated by zonal differentials can be connected,
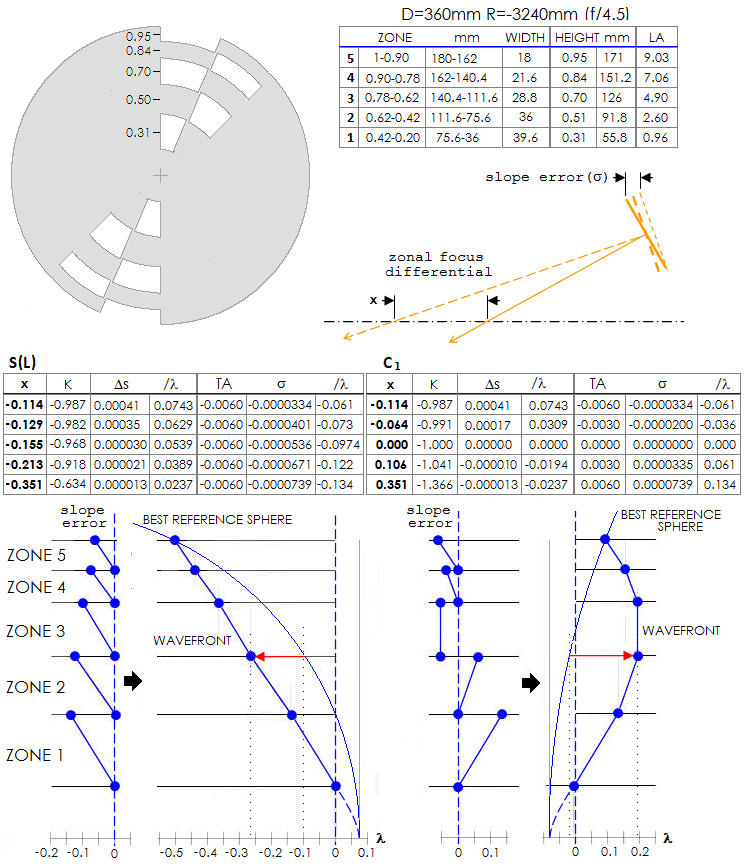
reconstructing approximation of the entire wavefront. It is illustrated here with a 5-zone mask, for the three
scenarios given above (L, which differes from S only in the sign, and C1), and 360mm f/4.5 mirror
(below; K is
the conic, Δs is the sagitta
differential, TA is the transverse aberration, and σ is the slope σ=(TA/R)z).
Reconstructed wavefront for S (short-focus) scenario, with all measurements at the negative limit, shows nearly linear deviation from spherical wavefront centered at the zero-deviation focus, from the most inner to the most outer zone; that implies non-conical surface. The cumulative deviation is over 0.5 wave, but most of it can be taken out by defocusing, i.e. measuring deviation with respect to a sphere with slightly shorter radius. The error is ~0.16 wave P-V (scenario L would have nearly identical wavefront profile, only of opposite sign). For C1 scenario, where surface has a conic profile, the wavefront profile closely resembles that of primary spherical aberration. The P-V wavefront error is somewhat larger here, ~0.21 wave P-V. Reconstructed wavefront is only a crude approximation, but it does indicate dominant shape of the actual wavefront. Correction terms for the longitudinal aberration As the basic relations for longitudinal defocus imply, Foucault test can be used for any conic shape. Longitudinal zonal defocus with respect to paraxial focus relates to the conic K and the vertex radius of curvature R as
LA = -K(ρd)2/R,
with ρ being the zonal height
normalized to 1 for the pupil radius d, for fixed light source,
and half as much when both, source and edge, are moving together (the
latter is the actual longitudinal aberration). The minus sign of defocus for K=-1 indicates that the outer zones focus
farther from paraxial focus, the result of over-correction. It is
arrived at by setting 2ψ=1 in
Eq. 9.1, and using
the resulting peak aberration coefficient,
Eq. 9.3, in
the relation for longitudinal aberration in
Eq. 10 (note
that when substituting for F in the latter,
F=-R/D due to the doubled mirror-to-image separation). It is particularly
convenient when testing prolate ellipsoids with reasonably close far
focus, when the light source is placed at the near focus, and null is
observed at the far focus. Obviously, this defocus figure is based
on the lower-order surface approximation.
Correction factor for the Foucault measurements that may become
significant with fast/large mirrors is related to the geometry of a ray
originating at the vertex center of curvature and reflected back above paraboloid's local radius.
This term is often called "higher order term"
but has nothing to do with higher order spherical aberration, i.e.
surface equation; it results from ray geometry, thus could be called "geometric
higher-order term" as opposed to the "surface higher-order
term", which is addressed next. While the incident and reflected angle
of this ray vs. local radius are identical, the latter will intersect
the axis slightly farther away from the local radius than the former,
due to it being positioned above the local radius. In other words, its
defocus vs. vertex center of curvature - where is located the source -
will be slightly greater than the sagitta for the zonal height doubled.
Δ'
Since the longitudinal
aberration proportional to the conic K, so is this geometric
higher order term, thus can be written as Δ'=-K(ρd)4/2R3. This term is negligible except
for very fast mirrors, for which the correct defocus is LA+Δ'.
Obviously, this factor does not apply with moving source, when defocus
is measured directly at the local radius.
Another possible correction factor is related to the surface (sagitta)
equation, and could be called "surface
higher-order term". From the geometry of ray originating at the intersection of local
radius of curvature and axis and reflecting back onto itself (hence for
moving source), it crosses axis at R-Kt from mirror vertex, R
being the vertex radius of curvature and t the sagitta for given
zonal height (for mirror oriented to left both R and t are
negative, thus they add up for K<0). Thus the longitudinal differential between
paraxial and zonal focus with moving source equals the zonal sagitta, given by (ρd)2/2R
for paraboloid. For fixed source, twice as much.
Thus, the higher-order longitudinal aberration terms for a paraboloid
are zero.
However, since the power series describing sagitta is:
t=(ρd)2/2R+(K+1)(ρd)4/8R3+(K+1)2(ρd)6/16R5+...,
conics other than paraboloid have non-zero higher-order terms adding to
the longitudinal defocus, with the defocus added given by:
Δ" =
(K+1)(ρd)4/8R3 + (K+1)2(ρd)6/16R5
+ ...
It is very unlikely these terms would have any significance with even very fast/large mirrors
for near-paraboloidal shape,
but it could increase test accuracy with such mirrors if the second term is
taken into account for figures that appreciably differ from parabolic.
Since this is correction to where the local radius intersects the axis,
these higher-order terms are also doubled for fixed source.
For very fast mirrors, the magnitude of both correction factors should
be checked to determine if their magnitude would be sufficient to make
the basic LA relation sufficiently different - as LA+Δ' (fixed
source, for evaluating this term alone), LA+Δ"
(moving source) or LA+Δ'+Δ" (fixed source, for evaluating
both terms combined) - to affect measurement accuracy.
It should be noted that both, OSLO Edu and ATMOS do show non-zero secondary
spherical aberration for paraboloid with source at the center of curvature,
opposite in sign to the primary spherical. Since R is constant
and surface equation t for parabola has no higher order terms,
this appears to be a glitch. For 200mm f/2.5
paraboloid the secondary spherical is 1/67 of the primary, which would
by somewhat less - probably closer to 1/100 - shorten the defocus for
the outer zone, nearly offsetting the geometric higher-order correction.
Since secondary spherical is in inverse proportion to the 5th power of
F-number, already at f/3 it would be
less than half as large, and roughly 50% smaller than the geometric
higher-order term.
Foucault test aberrations
By establishing focus locations of annular zonal openings for
non-spherical surfaces, the surface shape can be approximated with high
level of accuracy. Common consensus seems to be that the general limit
to a repeatable accuracy with the Foucault test is ~1/10 wave P-V on the
wavefront, assuming needed testing skills. In practice, the accuracy limit
vary with the type of deformation: it is to expect that it is higher for
the rotationally symmetrical overall figure, where needed surface
accuracy is only half that showing in the wavefront.
On the other hand,
Foucault's accuracy is generally lower for zonal, local and rotationally
asymmetrical figure errors, particularly astigmatism. It also
becomes less reliable for relative apertures significantly larger than
~f/4. Significant changes
in the wavefront and ray geometry for the object at the center of
curvature versus infinity, brings on quite a bit of change in surface
aberrations. The P-V
wavefront error of lower-order spherical
aberration at the best focus, from
Eq. 7 and
9, is given by: Ws = -KD4/256R3 = KD/2048F3, with K being the mirror conic, and F being the mirror focal number for object at infinity. For prolate ellipsoids, paraboloid and hyperboloids, the negative sign determined by the conic indicates over-correction. Comparing it with Eq. 66 shows that paraboloid with object at the center of curvature exerts the same amount of spherical aberration as a comparable sphere for object at infinity, only of opposite sign. However, since the effective focal ratio F has doubled, the geometric aberration has changed: as specified earlier, longitudinal spherical is larger by a factor of four vs. that for the corresponding sphere and object at infinity (L=D/32F for the diameter D in mm), while the transverse spherical is now doubled, keeping the same proportion to the Airy disc. The former changes in proportion to the square, and the latter in proportion to the cube of the zonal height. The wavefront aberration, transverse and longitudinal aberrations change in proportion to the fourth, third and second power of the zonal height, respectively. For the stop at the surface, coma with object at the center of curvature is cancelled, regardless of the conic. The wavefront error of astigmatism, on the other hand, doesn't change with object distance, remaining as given by Eq. 71.1. It quickly increases with angular separation between the source and mirror focus, which needs to be kept at a minimum in order to preserve best possible focus quality. Since this separation is the incidence angle (with respect to the axis passing through mirror center) doubled, the value corresponding to off-axis height h in the equation is s/2, s being the source-to-focus separation. Due to doubled mirror-to-image distance, the effective angle is yet another two times smaller, corresponding to s/4 off axis height at the infinity focus. Thus, replacing h with s/4 gives the RMS wavefront error of astigmatism induced as ω=s2/627DF3, for the aperture diameter D in mm (s is in mm as well) and infinity focal ratio F (in units of 550nm wavelength, ω=2.9s2/DF3; as little as 20mm source-to-focus separation with 200mm f/4 mirror induces 0.09 wave RMS error of lower-order astigmatism). For s and D in inches, ω=74s2/DF3. Unlike the wavefront aberration, the geometric aberrations of astigmatism does change due to the doubled effective focal ratio F for mirror with object at its center of curvature, with the longitudinal aberrations larger by a factor of four, and the transverse aberration nominally doubled. The wavefront error changes in proportion to the square of the zonal height, transverse aberration with the zonal height, and the longitudinal is, as expected, constant. Contrary to the common belief, mirror astigmatism can be detected with the Foucault setup (as well as Ronchi), even when quite low. Both, geometric and diffraction analysis (Astigmatism under the Foucault test, Linfoot, click on "print this article" for PDF) predict that astigmatism produces uneven intensity distribution along one of the two perpendicular (or nearly so, for less symmetrical forms) astigmatic axes, which has one side brighter, and the other darker than the rest of illuminated surface. Depending on its orientation in the setup, and the point of interception, this illumination asymmetry results on more or less obvious apparent rotation of the shadow (in the Ronchi, also depending on the orientation, it will cause either gradual change in line width, similar to the effect of spherical aberration - when the grating orientation coincides with that of astigmatic axes - or S-like line deformation when astigmatic axes are at 45 angle vs. grating). John Sherman's spot test web pages describe some practical approaches for detecting astigmatism in the Foucault or Ronchi setup, along with graphic illustrations. Quantifying astigmatism with either of the two tests is, however, more difficult. ASTIGMATISM IN THE FOUCAULT TEST Foucault test is known as insufficient at detecting astigmatic deformation of the test surface, but it does have the capability to detect relatively large errors, under certain conditions. Following two examples should illustrate more specifically its limitations in this respect. The first is a smaller, medium fast mirror, with which detection limit falls generally above the level of spherical aberration of the mirror at the r.o.c. The sensitivity is the lowest when astigmatic axis is aligned with the KE, and highest when it is at a 45-degree angle.  The other one is a large, fast mirror, with which the detection limit is, roughly, at half its spherical aberration at r.o.c. However, since it is several times higher than in the first example, the detection threshold is actually about twice larger astigmatic deformation. If compared to the Ronchi test, it is significantly less sensitive in this respect.  The astigmatism in these simulations is of saddle-like shape, which corresponds to the wavefront error at the best focus location. Actual surfaces commonly have cylindrical deformation, but the P-V error remains unchanged, only the RMS error is larger by a factor of √1.5. ◄ 4.8.1. Testing optical quality ▐ 4.8.3. Ronchi test ►
|
 FIGURE 52: The principle of the Foucault test.
Light reflected from mirror surface carries the information on geometric
properties of the reflecting surface: if it is perfect spherical, the
light from the entire surface will converge to a single aberration-free focus. If surface deviates from
spherical, focus location will vary with the zonal height. An opaque
thin plate with straight, sharp edge (usually some type of metal blade, called knife edge,
or KE for short) moving perpendicularly across the
focusing light in the proximity of focus location produces a shadow
moving across the surface; shape of the shadow tells instantly whether a
surface is spherical, with one unique focus for the entire surface, or
not.
FIGURE 52: The principle of the Foucault test.
Light reflected from mirror surface carries the information on geometric
properties of the reflecting surface: if it is perfect spherical, the
light from the entire surface will converge to a single aberration-free focus. If surface deviates from
spherical, focus location will vary with the zonal height. An opaque
thin plate with straight, sharp edge (usually some type of metal blade, called knife edge,
or KE for short) moving perpendicularly across the
focusing light in the proximity of focus location produces a shadow
moving across the surface; shape of the shadow tells instantly whether a
surface is spherical, with one unique focus for the entire surface, or
not.